Save Time. Teach more!
100% FREE BIOLOGY WORKSHEETS....
Practice worksheets covering Cell Biology, Human Biology, Molecular Biology, and more!
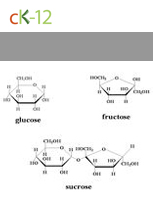
Carbohydrates
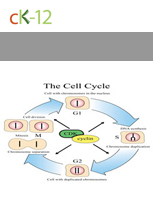
The life of a eukaryotic cell can be divided into 4 distinct phases, ending with cell division.
Cell Cycle
The life of a eukaryotic cell can be divided into 4 distinct phases, ending with cell division.
Cell Division
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis:
All cells reproduce by dividing into two genetically identical daughter cells.
Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration:
The cellular process which transfers chemical energy from glucose to ATP.
Characteristics of Life
What characteristics do all living organisms share? We look at the characteristics of life including respiration, growth, and responding to their environment.
Chemistry of Life
The rate at which radioisotopes break down into smaller atomic nuclei.
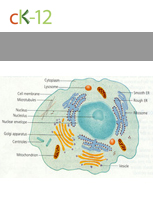
Common Parts of the Cell
Cellular Structure and Function
How a cell functions is directly related to its structure. A nerve cell differs from a skin cell in how it looks and what is does.
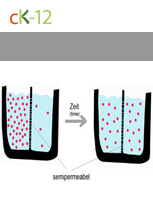
Diffusion
Introduces diffusion and osmosis and how the concepts relate to cells.
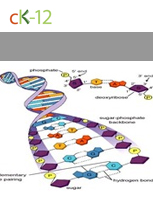
DNA Structure and Replication
Describes the DNA double helix and how DNA is copied.
DNA, the Genetic Material
Discuss identification of the genetic material.
Gregor Mendel and Genetics
Genetics is the study of heredity in organisms and was pioneered by Gregor Mendel's experiments.
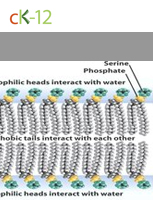
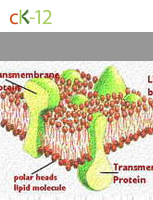
Phospholipid Bilayers
A membrane where phospholipid molecules orient to provide qualities necessary to maintain a cell in a water-based environment.
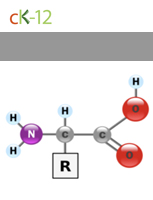
Proteins
Made of smaller units called amino acids, proteins provide energy for cells and perform many cellular functions.
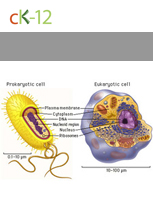
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane bound nucleus. Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles.
Scientific Methods
Scientific experiments involve observation, experimentation, and analysis of results.
Significance of Carbon
Carbon is an element that has unique properties (exceptional ability to form bonds) that makes it essential to life on earth.
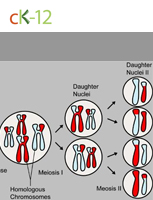
Meiosis
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis
A type of cell division that produces haploid cells from a diploid parent cell.
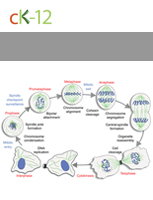
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis
The process by which eukaryotic cells divide to produce identical daughter cells.
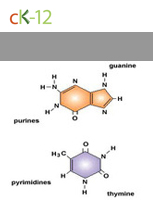
Nucleic Acids
Organic compounds that consist of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Examples: DNA, RNA.
Lipids
Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen that do not mix with water.
CK-12 Biology
CK-12 Biology is a high school FlexBook® textbook covering cell biology, genetics, evolution, ecology, microorganisms, fungi, plants, invertebrates, vertebrates...
CK-12 Biology Advanced Concepts
Biology concepts for high school.
CK-12 Biology Concepts
Biology concepts for high school.
CBSE Biology Book Class 9
This biology text was created using CK-12 resources to be seed content for a complete Biology Class 9 course for CBSE students.
CBSE Biology Book Class 11
This biology text was created using CK-12 resources to be seed content for a complete Biology Class 11 course for CBSE students.
CBSE Biology Book Class 12
This biology text was created using CK-12 resources to be seed content for a complete Biology Class 12 course for CBSE students.
Human Biology - Breathing
The Breathing Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Circulation
The Circulation Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Digestion and Nutrition
The Digestion and Nutrition Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Ecology
The Ecology Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Genetics
The Genetics Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Nervous System
The Nervous System Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Reproduction
The Reproduction Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Sexuality
The Sexuality Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Lives of Cells
The Lives of Cells Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
Human Biology - Your Changing Body
The Your Changing Body Student Edition book is one of ten volumes making up the Human Biology curriculum, an interdisciplinary and inquiry-based approach to the study of life science.
CK-12 Life Science Concepts For Middle School
Life Science concepts for middle school.
CK-12 Life Science For Middle School
CK-12 Life Science For Middle School covers: Cell Biology, Genetics, Evolution, Prokaryotes, Protists, Fungi, Plants, The Animal Kingdom, The Human Body, and Ecology.